Prophylaxis and therapy of diarrhea with S. boulardii
Co-medication of Helicobacter-pylori “triple therapy” regimens
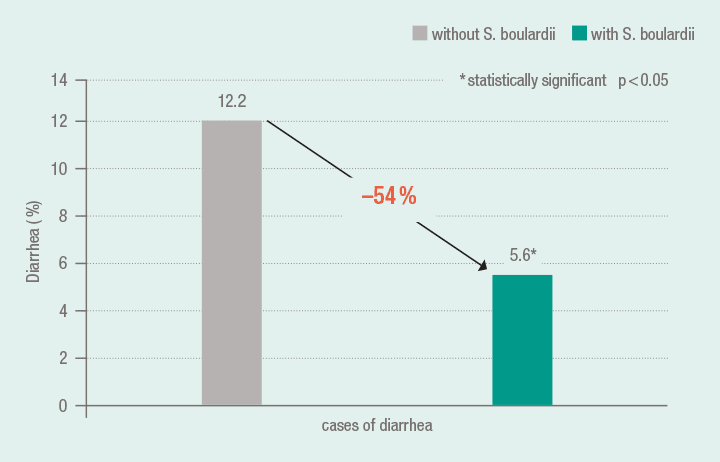
In the context of a meta-analysis (5 studies, n = 1307 patients) the data of 1215 patients from 4 studies were evaluated, who received eradication therapy due to Helicobacter pylori infection (proton pump inhibitor, clarithromycin or amoxicillin/clarithromycin). By the adjuvant administration of S. boulardii in the triple therapy regimen, the risk of treatment-related diarrhea was lowered from 12.2 % to 5.6 %. A further result of this meta-analysis was that in comparison to controls the eradication rate of Helicobacter by the additional application of S. boulardii was increased (S. boulardii: 80 %; controls: 71 %). For this purpose, 4 studies were evaluated with the data from 915 patients (n = 460 treated with S. boulardii, n = 455 treated with placebo).16
The therapeutic benefit of adjuvant administration of S. boulardii in patients under classical triple therapy regimen was confirmed in a further clinical trial by Kyriakos et al.17. This clinical study also showed the improvement of eradication rate of Helicobacter as well as a reduction of therapy-associated side-effects, in particular diarrhea.
The effect of S. boulardii on the eradication rate was further studied in asymptomatic children with a positive stool exam for H. pylori antigens. In such a placebo controlled clinical trial it was shown, that S. boulardii (Yomogi) is capable to cause a slight but significant decrease of H. pylori stool antigen19.
Significantly fewer cases of diarrhea under triple therapy with co-medication using S. boulardii 16
S. boulardii significantly improves the tolerability of triple therapy
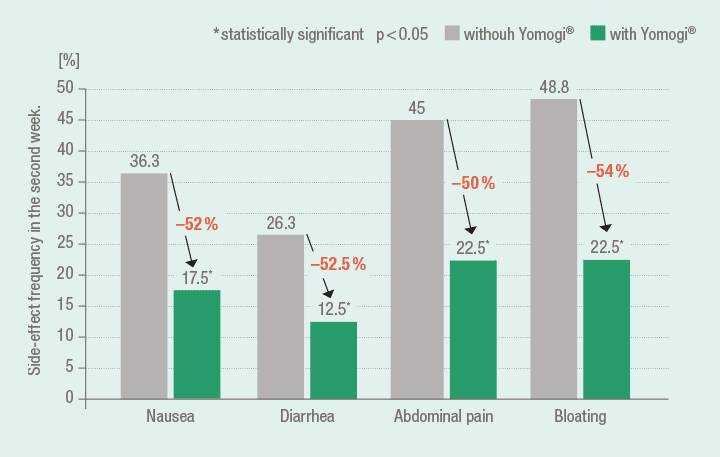
A significant improvement in the tolerability of triple therapy using adjuvant administration of S. boulardii was substantiated by a study from Zojaji et al.18 (Group A (n = 80) and B (n = 80): amoxicillin (1000 mg, b.i.d.), clarithromycin (500 mg, b.i.d.), omeprazole (20 mg, b.i.d.) for 14 days; co-medication Group A: Yomogi (250 mg, b.i.d.)).
Significantly fewer cases with side-effects during triple therapy with co-medication using Yomogi 18
Further drug-associated diarrhea
Other medicines can also cause gastrointestinal distress with diarrhea. These include cytostatic drugs (such as methotrexate, cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil) or even high-dosed mineral supplements (such as magnesium) and proton pump inhibitors.
16) Szajewska H, Horvath A, Piwowarczyk A. Meta-analysis: the effects of Saccharomyces boulardii supplementation on Helicobacter pylori eradication rates and side effects during treatment. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2010;32(9):1069–1079.
17) Kyriakos N, Papamichael K, Roussos A. Theodoropoulos I, Karakoidas C, Smyrnidis A, Archavlis E, Lariou K, Mantzaris GJ. A Lyophilized Form of Saccharomyces Boulardii Enhances the Helicobacter pylori Eradication Rates of Omeprazole-Triple Therapy in Patients With Peptic Ulcer Disease or Functional Dyspepsia. Hospital Chronicles. 2013;8:127–133.
18) Zojaji H, Ghobakhlou M, Rajabalinia H, Ataei E, Sherafat SJ, Moghimi-Dehkordi B and Bahreiny R. The efficacy and safety of adding the probiotic Saccharomyces boulardiito standard triple therapy for eradication of H.pylori: a randomized controlled trial. Gastroenterol Hepatol Bed Bench. 2013;6(Suppl 1):S99–S104.
19) Namkin K, Zardast M, Basirinejad F. Saccharomyces boulardii in Helicobacter pylori eradication in children: A randomized trial from Iran. Iran J Pediatr. 2016; 26(1): e3768. doi:10.5812/ijp.3768.
